Anotace:
Napětí v betonářské výztuži ss1 může být stanoveno buď výpočtem ze zadaného ohybového momentu MEd
nebo jej můžete zadat ručně (při MEd = 0).
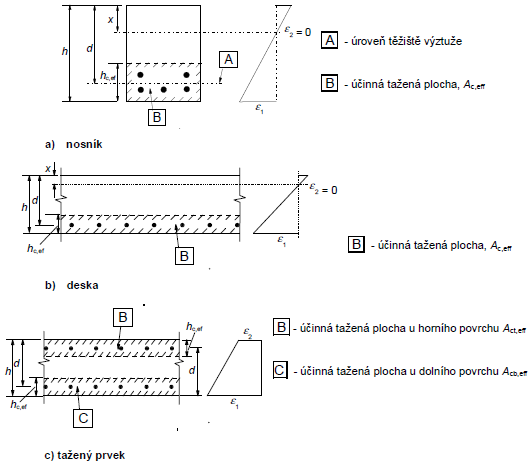
Ap‘ je plocha předem nebo dodatečně napínané výztuže ležící v ploše Ac,eff
Ac,eff účinná plocha taženého betonu obklopující betonářskou nebo předpínací výztuž o výšce hc,ef (viz obrázek 7.1)
hc,ef je menší z hodnot:
Obrázek 7.1 - Účinná tažená plocha (typické případy)
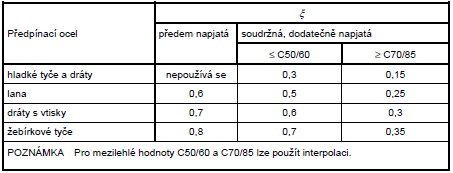
x je poměr pevnosti v soudržnosti předpínací a betonářské výztuže podle tabulky 6.2 v 6.8.2:
k1 je součinitel, kterým se zohledňují vlastnosti soudržné výztuže:
= 0,8 pro pruty s velkou soudržností;
= 1,6 pro pruty s hladkým povrchem (např. předpínací vložky);
k2 je součinitel, kterým se zohledňuje rozdělení poměrného přetvoření:
= 0,5 pro ohyb;
= 1,0 pro prostý tah.
Pro případy mimostředného tahu nebo pro místní oblasti se mají použít mezilehlé hodnoty k2, které se vypočítají podle následujícího vztahu:
k2 = (e1 + e2)/2e1
kde e1 je větší a e2 menší tahové poměrné přetvoření na okrajích vyšetřovaného průřezu,stanovené v průřezu, který je celý oslaben trhlinou.
Hodnoty k3 a k4, které se použijí v příslušném státě, lze nalézt v národní příloze. V ČR platí doporučené hodnoty (viz NA 2.74):
k3 = 3,400
k4 = 0,425.
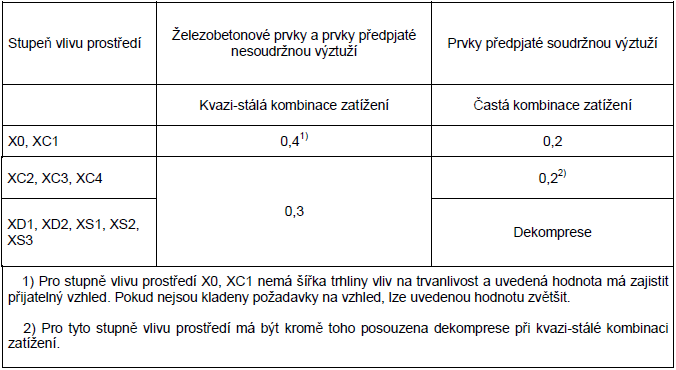
Tabulka 7.1N - Doporučené hodnoty wmax (mm)
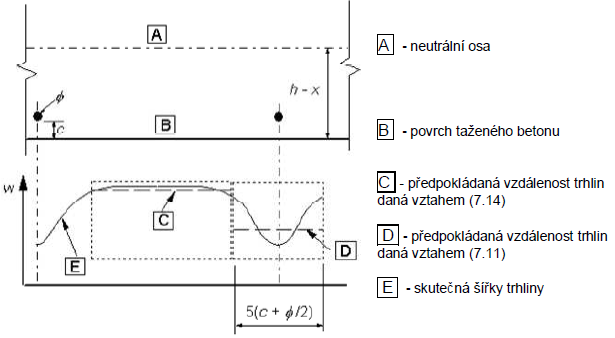
Obrázek 7.2 - Šířka trhliny na povrchu betonu v závislosti na vzdálenosti od prutu