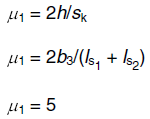Documentation
This document contains all National annex values, which are used in SDF - Basic package
The characteristic values of snow load on the ground sk in Slovenia should be obtained from the map and formula.
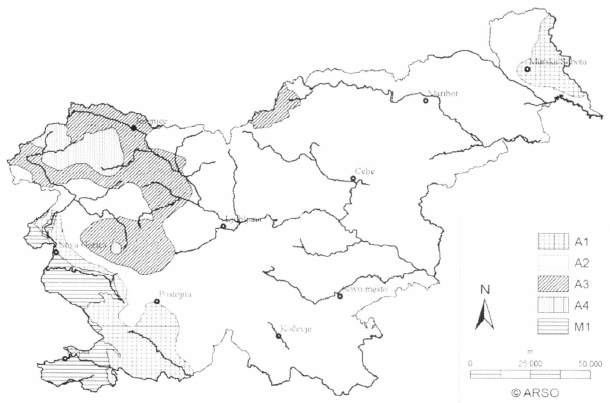

sk have to be bigger than 1,2 kN/m2 in Alpen region.
Clause 4.3 Treatment of exceptional snow loads on the ground, paragraph (1)
Recommended value of the coefficient should be used in altitude A ≥ 1500 m, Cesl = 2,0
Clause 5.2 Load arrangements, paragraph (7)
Standard values are used
Clause 5.2 Load arrangements, paragraph (8)
Ct can be between 0 and 1 as recommended for roofs with high thermal transmittance.
Clause 5.3.3 Pitched roofs, paragraph (4)
Standard drifted load arrangement is used.
Clause 5.3.4 Multi-span roofs, paragraph (3)
Annex B can be used in the sites with altitude A ≥ 1500 m above sea level.
Standard drifted snow load is used in all other cases.
Annex B:

Shape coefficient μ1 is determined as the least value of:
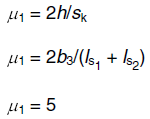
Drift lengths are determined as:

Clause 5.3.4 Multi-span roofs, paragraph (4)
If α ≥ 60�, the coefficient μ2 = 1,6
Clause 5.3.5 Cylindrical roofs, paragraph (1)
μ3,max = 2,0
Clause 5.3.5 Cylindrical roofs, paragraph (3)
Standard drifted snow load is used.
Clause 5.3.6 Roof abutting and close to taller construction works, paragraph (1)
0,8 ≤ μw ≤ 4,0
5 m ≤ ls ≤ 15 m
Annex B can be used in the sites with altitude A ≥ 1500 m above sea level.
Clause 5.3.6 Roof abutting and close to taller construction works, paragraph (3)
Annex B can be used in the sites with altitude A ≥ 1500 m above sea level.
Annex B can be used also for construction close to taller building, if constructions are less than 1,5 m away.
Standard drifted snow load is used in all other cases.
Annex B:

Drift length ls is the least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Table 3: Shape coefficients for exceptional snow drift for roofs abutting and close to taller structures
| μ1 |
μ3 |
μ3{[30 - α]/15} |
0 |
0 |
| μ2 |
μ3 |
μ3 |
μ3{[60 - α]/30} |
0 |
μ3 is the least value of 2h/sk, 2b/ls or 8.
b is larger of b1 or b2.
ls it she least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Clause 6.2 Drifting at projections and obstructions, paragraph (2)
Annex B can be used in the sites with altitude A ≥ 1500 m above sea level.
Standard drifted snow load is used in all other cases.
Annex B:
If the vertical elevation against which a drift could form is not greater than 1 m2, the effect of drifting can be ignored.
This clause applies to:
- Drifting against obstructions not exceeding 1 m in height.
- Drifting on canopies, projecting not more than 5m from the face of the building over doors and loading bays, irrespective of the height of the obstruction.
- Slender obstructions over 1 m high but not more than 2 m wide, may be considered as local projections. For this specific case h may be taken as the lesser of the projection height or width perpendicular to the direction of the wind.

The shape coefficient is determined as the least value of:
μ1 = 2h1/sk or 5
μ2 = 2h2/sk or 5
In addition, for door canopies projecting not more than 5 m from the building, μ1 should not exceed 2b/ls1, where b is the larger of b1 and b2.
The drift length (lsi) is taken as the least value of 5h or bi, where i = 1 or 2 and h ≤ 1 m.

The shape coefficient is determined as the least value of:
μ1 = 2h/sk
μ1 = 2b/ls
μ1 = 8
The drift length ls should be taken as the least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Clause 6.3 Snow overhanging the edge of a roof, paragraph (1)
Clause should be used for sites at altitudes greater than 400 m above sea level.
Clause 6.3 Snow overhanging the edge of a roof, paragraph (2)
The coefficient k remains unchanged, however d = s/3 kN/m3
where:
s = μ•sk in kN/m3
μ is coefficient on the adjanced roof.