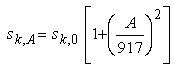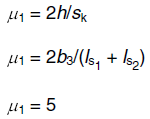Documentation
This document contains all National annex values, which are used in SDF - Basic package
Clause 4.1 Characteristic values, paragraph (1)
The characteristic snow load on the ground in a location depends on the zone to which the site and the elevation of the site above sea level.
Snow zones:
Zone A: Countries Arcadia, Elis, Laconia, Messinia and all islands except the Sporades and Evia
Zone C: Countries Magnesia Fthiotida, Karditsa, Trikala, Larissa, Sporades and Evia
Zone B: Rest of Country
For each zone, the characteristic snow load on the ground, sk,A is given by the following equation:
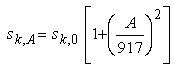
Where:
sk,0 is the characteristic snow load on the ground located at sea level (A = 0)
A is the altitude of the site above sea level (in m). The altitude A is rounded to 100 m. The altitude is rounded to the next higher hundred.
Table 1: Values of characteristic snow load on the ground sk,0 at sea level (A = 0)
Clause 4.3 Treatment of exceptional snow loads on the ground, paragraph (1)
Recommended value is used. Cesl = 2,0
Clause 5.2 Load arrangements, paragraph (7)
Recommended values of Ce and topographies are used.
Clause 5.2 Load arrangements, paragraph (8)
Ct = 1,0 for all roof materials
Clause 5.3.3 Pitched roofs, paragraph (4)
Standard drifted load arrangement is used.
Clause 5.3.4 Multi-span roofs, paragraph (3)
Annex B should be used instad of standard load arrangement in case of exceptional snow drift. Standard drifted load is recommended in other cases.
Annex B:

Shape coefficient μ1 is determined as the least value of:
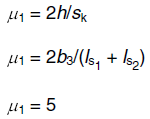
Drift lengths are determined as:

Clause 5.3.4 Multi-span roofs, paragraph (4)
Recommended value is used.
Clause 5.3.5 Cylindrical roofs, paragraph (1)
Recommended value is used. μ3,max = 2,0
Clause 5.3.5 Cylindrical roofs, paragraph (3)
Standard drifted snow load is used.
Clause 5.3.6 Roof abutting and close to taller construction works, paragraph (1)
Recommended range is used. 0,8 ≤ μw ≤ 4,0
Clause 5.3.6 Roof abutting and close to taller construction works, paragraph (3)
Annex B should be used instad of standard load arrangement in case of exceptional snow drift. Standard load arrangement is recommended in other cases.
Annex B:

Drift length ls is the least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Table 3: Shape coefficients for exceptional snow drift for roofs abutting and close to taller structures
| μ1 |
μ3 |
μ3{[30 - α]/15} |
0 |
0 |
| μ2 |
μ3 |
μ3 |
μ3{[60 - α]/30} |
0 |
μ3 is the least value of 2h/sk, 2b/ls or 8.
b is larger of b1 or b2.
ls it she least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Clause 6.2 Drifting at projections and obstructions, paragraph (2)
Annex B should be used instad of standard load arrangement in case of exceptional snow drift. Standard load arrangement is recommended in other cases.
Annex B:

The shape coefficient is determined as the least value of:
μ1 = 2h1/sk or 5
μ2 = 2h2/sk or 5
In addition, for door canopies projecting not more than 5 m from the building, μ1 should not exceed 2b/ls1, where b is the larger of b1 and b2.
The drift length (lsi) is taken as the least value of 5h or bi, where i = 1 or 2 and h ≤ 1 m.

The shape coefficient is determined as the least value of:
μ1 = 2h/sk
μ1 = 2b/ls
μ1 = 8
The drift length ls should be taken as the least value of 5h, b1 or 15 m.
Clause 6.3 Snow overhanging the edge of a roof, paragraph (1)
The calculation of snow load due to overhang is perform in locations with altitude above 800 m.
Clause 6.3 Snow overhanging the edge of a roof, paragraph (2)
The recommended procedure for calculation coefficient is used and bulk weight density of snow γ = 3 kN/m3 should be used for the assessment of the depth of the snow cover.